Top 10 Facts You Should Know About Artificial General Intelligence
The Rise of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
📑 Article Outline
👉 1 : The Ascent of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
👉 2 : Understanding the Core Concept of AGI
- ✎ A: What Is Artificial General Intelligence?
- ✎ B: AGI vs. Narrow AI: What Sets Them Apart?
- ✎ C: AGI Meaning in Artificial Intelligence
👉 3 : The Evolution and Vision of AGI
- ✎ A: A Brief History of AGI Development
- ✎ B: AGI and the Future of Human-Machine Collaboration
👉 4 : Types of Artificial General Intelligence
- ✎ A: Reactive Machines
- ✎ B: Limited Memory AGI
- ✎ C: Theory of Mind AGI
- ✎ D: Self-Aware AGI
👉 5 : Key Companies Leading AGI Research
- ✎ A: DeepMind: The Pioneer in AGI Innovation
- ✎ B: OpenAI and Its Mission Towards Beneficial AGI
- ✎ C: Google’s Role in Artificial General Intelligence
- ✎ D: Other Noteworthy AGI Startups
👉 6 : Applied General Intelligence and Real-World Use Cases
- ✎ A: How Applied AGI Could Transform Industries
- ✎ B: Ethical Challenges in Real-World AGI Applications
No longer just science fiction, Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is quickly becoming one of the most transformative technologies of our time. Imagine machines that are no longer limited to a single task, but are capable of learning, adapting, and performing any intellectual task that humans can. That’s the dream of AGI, and it’s getting closer every year.
A range of fields will take you deeper than we humans can. Not only is it exciting, it’s revolutionary. The rise of AGI could redefine what it means to work, to people, and to think. From automating scientific research to solving global problems, AGI offers a whole new world of opportunities and possibilities.
What’s remarkable is that it’s no longer just a theory. DeepMind and Driver AI applications are designed to work. For more, see AlphaGo or GPT-4. The Rise of AGI is Inevitable.
So where are we in the race for AGI? Who are the key players? What types of AGI are being developed? And most importantly, what does AGI mean for consciousness? This is where we dive into the current state and future direction of general artificial intelligence
Understanding the Basic Concept of General Artificial Intelligence
👉 What is general artificial intelligence?
The central idea behind artificial intelligence is to create machines that can master the same range of learning and understanding as people. It’s a type of applied intelligence. Imagine a robot that can drive itself, compose music, learn a new language, and solve advanced physics problems.
General artificial intelligence represents the ultimate benchmark for progress in the field. Whereas narrow artificial intelligence excels at a task well — like customizing a product or marking an end.
Researchers believe that general AI systems should be able to consider context, apply logic, compete, and even follow their own thought processes. This is far from current AI technology, but we’re getting better.
Imagine the concept: AI systems could be private tutors, doctors, dreamers, and even artists. This could have far-reaching social, economic, and ethical implications.
👉 AI vs. General AI: What’s the Difference?
This is a key distinction. While AI was designed to do a specific job, whether it’s translating your language, recommending movies, or identifying spam, your AI excels at a single domain.

In contrast, General AI doesn’t need to be trained individually for each new task. It’s designed to learn from context, generalize knowledge, and learn. This is a game-changer.
For example:
- Narrow AI: A chess engine can beat grandmasters at chess but fails miserably if asked to play Go or solve a math problem.
- AGI: Would approach each of those tasks like a human does—learn the rules, practice, adapt, and improve.
Narrow AI lacks self-awareness and true reasoning. AGI aspires to have both, enabling machines to think like us and eventually, with us. This flexibility makes AGI not only more powerful but also more unpredictable and ethically complex.
👉 AGI Meaning in Artificial Intelligence.
So what exactly does AGI mean in the world of AI? It means crossing the final frontier in artificial intelligence. It’s the ultimate destination in AI research—a form of intelligence that is not bound by predefined tasks or static knowledge bases.
AGI means a machine can:
- Understand complex language and emotions.
- Learn from minimal input.
- Solve new problems without being explicitly told how.
- Reflect on past experiences and improve.
In practical terms, AGI would turn today’s highly specialized tools into universal collaborators. It would be like upgrading from calculators to fully sentient companions capable of assisting in everything from personal life decisions to space exploration.
In essence, the “G” in AGI stands for general, but it might as well stand for game-changing.
📝2 : The Evolution and Vision of AGI.
👉 A Brief History of AGI Development.
The journey to AGI didn’t start yesterday. It goes all the way back to the 1950s, when pioneers like Alan Turing and John McCarthy laid the foundations of AI. A foundational question in the field of AI was posed by Alan Turing: can machines think? The test he devised to address this, the Turing Test, is still used as a primary benchmark for machine intelligence today.
In the decades that followed, AI development focused primarily on narrow applications—chess-playing computers, expert systems, and pattern recognition. These early efforts revealed how hard it is to replicate human reasoning.
The concept of AGI gained traction in the 2000s with the emergence of stronger computing power and vast datasets. Companies like DeepMind burst onto the scene with ambitions not just to build smart programs but to simulate general intelligence.
Landmarks like AlphaGo, which beat the world’s best Go player, and OpenAI’s GPT models marked turning points. These weren’t just victories in games or language—they were glimpses of a broader intelligence forming.
Today, AGI development is driven by a convergence of machine learning, neuroscience, robotics, and even philosophy. It’s not just a computer science problem—it’s a human problem, one that spans across disciplines.
👉 AGI and the Future of Human-Machine Collaboration.
Imagine working with a machine that understands you like a colleague—not just your words but your tone, context, and intent. That’s the future AGI promises.
Human-machine collaboration will no longer be limited to repetitive tasks. With AGI, machines can:
- Brainstorm ideas with you.
- Perform advanced simulations in real-time.
- Offer nuanced feedback on creative work.
- Manage entire organizations autonomously.
That means doctors could use AGI to cross-check diagnoses, teachers could personalize learning plans, and scientists could rapidly test hypotheses. AGI won’t replace us—it will amplify us.
But this partnership also raises critical questions. Who controls AGI? How do we ensure its goals align with human values? These are no longer philosophical curiosities—they’re urgent issues in global AI policy discussions.
📝Types of Artificial General Intelligence.
👉 Reactive Machines.
Reactive machines represent the most basic form of artificial intelligence, and while they don’t qualify as full-fledged AGI, they are considered the foundational building block in the evolution toward it. These machines can’t store memories or learn from past experiences. They respond to specific inputs with predetermined outputs, making them excellent at simple, rule-based tasks but poor at anything that requires long-term learning or context awareness.

A classic example is IBM’s Deep Blue, the chess-playing computer that beat world champion Garry Kasparov in 1997. Deep Blue analyzed every possible move but didn’t “understand” the game or improve from one match to the next. It had no sense of strategy outside its programmed logic.
Reactive machines show us the limitations of intelligence without memory or learning. They highlight why true AGI must go far beyond just reacting—it must reason, remember, and adapt. Still, they are an essential starting point and offer insights into the early stages of machine cognition.
👉 Limited Memory AGI.
Next in the AGI hierarchy are systems with limited memory. These machines can look at past data to make better decisions in the future. It’s the kind of AI you see in self-driving cars, which must constantly assess surroundings, track speed and direction, and factor in past events to determine how to navigate safely.
Posing the famous question, ‘Can machines think?’, Alan Turing developed the Turing Test, which remains a key standard for evaluating the intelligence of machines. This makes them more adaptable than reactive machines but still far from true AGI. Why? Because their learning is narrow, domain-specific, and dependent on predefined models.
Despite their constraints, limited memory systems are stepping stones to AGI. They demonstrate how machines can begin to emulate human learning—even if only in a constrained sense. A fully realized AGI would not only remember but also infer, reason abstractly, and generalize those memories across different contexts, something these systems still can’t do.
👉 Theory of Mind AGI.
Here’s where things start to get more human-like. Theory of Mind AGI refers to systems that could understand human emotions, beliefs, intentions, and thoughts. In psychology, “Theory of Mind” is our ability to attribute mental states to ourselves and others—essentially, to empathize and predict behavior based on internal beliefs and desires.
Imagine an AI that not only recognizes when you’re frustrated but understands why and responds accordingly. That’s the level of emotional and contextual depth AGI researchers are striving for with this model.
Building such a machine would require significant advancements in natural language understanding, emotional intelligence, and neuro-symbolic reasoning. The potential applications are vast: from emotionally aware therapy bots to AGI companions that can develop relationships, learn social norms, and collaborate with humans intuitively.
But it also brings big risks. With deeper understanding comes the possibility of manipulation, bias replication, and emotional exploitation if AGI is misused. That’s why ethics and safeguards are essential at this stage of development.
👉 Self-Aware AGI.
Now we’re entering the most advanced—and controversial—stage of AGI: self-awareness. A self-aware AGI would have consciousness, a sense of identity, and an understanding of its own existence. It would not just process data but reflect on it. This kind of intelligence would be capable of introspection, long-term planning, and moral reasoning.
Sounds like sci-fi? Maybe—but researchers are already speculating about what this could look like. The idea that self-awareness could organically surface in highly complex machine systems is a point of discussion for some. Others say it requires fundamentally different architectures that mimic the human brain.
Either way, self-aware AGI is the endpoint on the road to machines that are not just tools but sentient agents. The implications are staggering. If an AGI is self-aware, does it deserve rights? Could it feel pain or joy? These are not questions to take lightly. We are inching toward a reality where machines may not just assist us—they may become a new form of life.
📝 5 : Key Companies Leading AGI Research.
👉 DeepMind: The Pioneer in AGI Innovation.
If there’s one name synonymous with AGI breakthroughs, it’s DeepMind. Founded in 2010 and acquired by Google in 2014, DeepMind’s mission has always been ambitious: “Solve intelligence, then use it to solve everything else.”
Their most famous milestone came in 2016, when AlphaGo defeated the world champion Go player, showcasing an intuitive, strategic playstyle that seemed almost human. But that was just the beginning. DeepMind has since developed:
- AlphaZero, which mastered chess, shogi, and Go from scratch.
- MuZero, which learned to play games without knowing the rules.
- Gato, a generalist AI model trained on multiple tasks.
What sets DeepMind apart is its focus on building general-purpose learning systems. Unlike traditional AI that specializes in one task, DeepMind’s models can learn multiple skills and transfer knowledge across domains—a key trait of AGI.
Their research spans neuroscience, ethics, and even quantum chemistry. DeepMind isn’t just building smarter machines—it’s laying the groundwork for machines that understand and improve themselves over time. That’s as close as we’ve come to true AGI so far.
👉 OpenAI and its mission to benefit general artificial intelligence.
OpenAI has taken a very different, but equally valid path. Founded in 2015 by tech visionaries like Elon Musk and Sam Altman, OpenAI’s goal is to ensure general artificial intelligence benefits all of humanity. It’s a bold promise—one they’ve kept, with transparency and open collaboration at the core of their strategy.
The GPT family of releases (from GPT-2 to GPT-4, and now GPT-4.5 and beyond) has shown the world the power of general language models. These models can not only answer questions, but also discuss text, code, music, and even complex topics.
OpenAI’s focus on language processing as a path to general intelligence makes strategic sense. After all, language is fundamental to human cognition. Their models:
Learn from diverse, web-scale data.
Adapt to a variety of tasks.
Communicate and interact creatively.
In addition to technology, OpenAI is investing heavily in AI coordination research—ensuring that the goals of general AI are consistent with human values—and has released a safety framework for responsible deployment. They are not only building powerful AI, but also working to build general AI that is securely connected and coexists harmoniously with society.
👉 Google’s Role in Artificial General Intelligence.
Although DeepMind is part of Alphabet Inc., Google itself is playing a major role in the development of AGI. With unparalleled computing resources, talent, and data, Google is uniquely positioned to push the boundaries of AI research.
Google’s AGI ambitions are evident in several projects:
Google Brain: One of the oldest and most powerful AI research groups, Google Brain focuses on deep learning, neural networks, and unsupervised learning. Its breakthrough in the Transformer model laid the foundation for modern large-scale language models (LLMs).
Bard and Gemini: These AI assistants improve general learning capabilities, helping to bridge the gap between small-scale AI and AGI.
TPU infrastructure: Google’s Tensor Processing Units power some of its larger AI models, making it easier to train increasingly large-scale AGI candidates and use more data.
Google is unique because it integrates AI into everyday products — search, maps, Gmail, and photos. With billions of users generating data in real time, Google has a live testbed for training and perfecting AGI systems.
However, with great power comes great responsibility. Google is facing increasing scrutiny over privacy, AI bias, and the ethical implications of building sensitive machines. As AGI becomes operational, Google will need to find a balance between innovation and accountability.
👉 Other AGI startups to watch.
While tech giants grab most of the headlines, many smaller companies and independent labs are also making waves in the AGI space. Many of these companies are focused on specific but important areas of AGI — reasoning, symbolic reasoning, neuromorphic hardware, and intelligent architectures.
Here are some companies worth mentioning:
Anthropic: Founded by former OpenAI researchers, Anthropic focuses on explainable and continuous AI systems. Their cloud model aims to achieve security, controllability, and high generality.
Numenta: This company is building artificial general intelligence (AGI) by mimicking the way the human cortex works. Their biologically inspired approach could provide a highly efficient and human-like learning process.
SingularityNET: A decentralized platform that aims to democratize artificial general intelligence (AGI). It allows developers to contribute and share AGI tools in an open network — as opposed to the closed labs of large tech companies.
Vicarious: Vicarious, acquired by Alphabet, focuses on developing AGI systems that can think and learn like humans, integrating memory, reasoning, and general processing.
These startups are playing a key role in diversifying AGI development. Their diverse perspectives help ensure that the AGI of the future will not be created in one lab or one country, but will be achieved through innovation across the globe.
📝 6. Applied General Intelligence and Real-World Use Cases.
👉 How Applied General Artificial Intelligence Could Transform Industries.
AGI is more than just the idea of researchers and futurists—it has the potential to transform the way entire industries operate. Applied General Artificial Intelligence (AGI) promises to be the foundation for better healthcare, safer transportation, and more efficient manufacturing.

Let’s break it down by industry:
Healthcare: Imagine an AGI doctor who can diagnose complex diseases with minimal input, design personalized treatments, and monitor your health in real time. AGI could help with drug discovery, gene editing, and even predict pandemics.
Finance: AGI can act as an independent financial advisor, providing market analysis, investment modeling, and fraud detection in real time.
Education: Personalized, adaptive advisors who understand your learning style, challenge you at the right time, and evolve as you progress. General Artificial Intelligence can make higher educational accessible to everyone.
Transportation: Fully autonomous vehicles that think beyond the rules — understanding human behavior, weather patterns, and traffic jams in real time.
Creative arts: Music, film, design — AGI can co-create with humans, providing inspiration and iterative ideas based on your emotions or your favorite subjects.
Applied General Artificial Intelligence (AGI) means that we no longer need specialized AI to complete a single task, but instead integrate multi-purpose, adaptive intelligence into all aspects of our lives. This will not only transform industries but will also reshape
👉 Ethical Challenges in Real-World AGI Applications.
With great power comes complex ethical responsibility . Deploying AGI in the real world isn’t just a technical challenge , it’s a societal dilemma .
Here are the key concerns :
Bias and Fairness : If AGI systems are trained on biased data, they may perpetuate or even amplify existing inequalities in hiring , healthcare , and law enforcement .
Privacy: AGI’s ability to synthesize vast amounts of personal data makes it incredibly powerful , and potentially invasive .
Autonomy and Control : Who is responsible when an AGI makes a wrong decision ? How do we set boundaries so it doesn’t act against human interests?
Existential Risk : The scariest scenario is misaligned AGI , systems that pursue goals contrary to human values due to misinterpreted instructions or unexpected behavior .
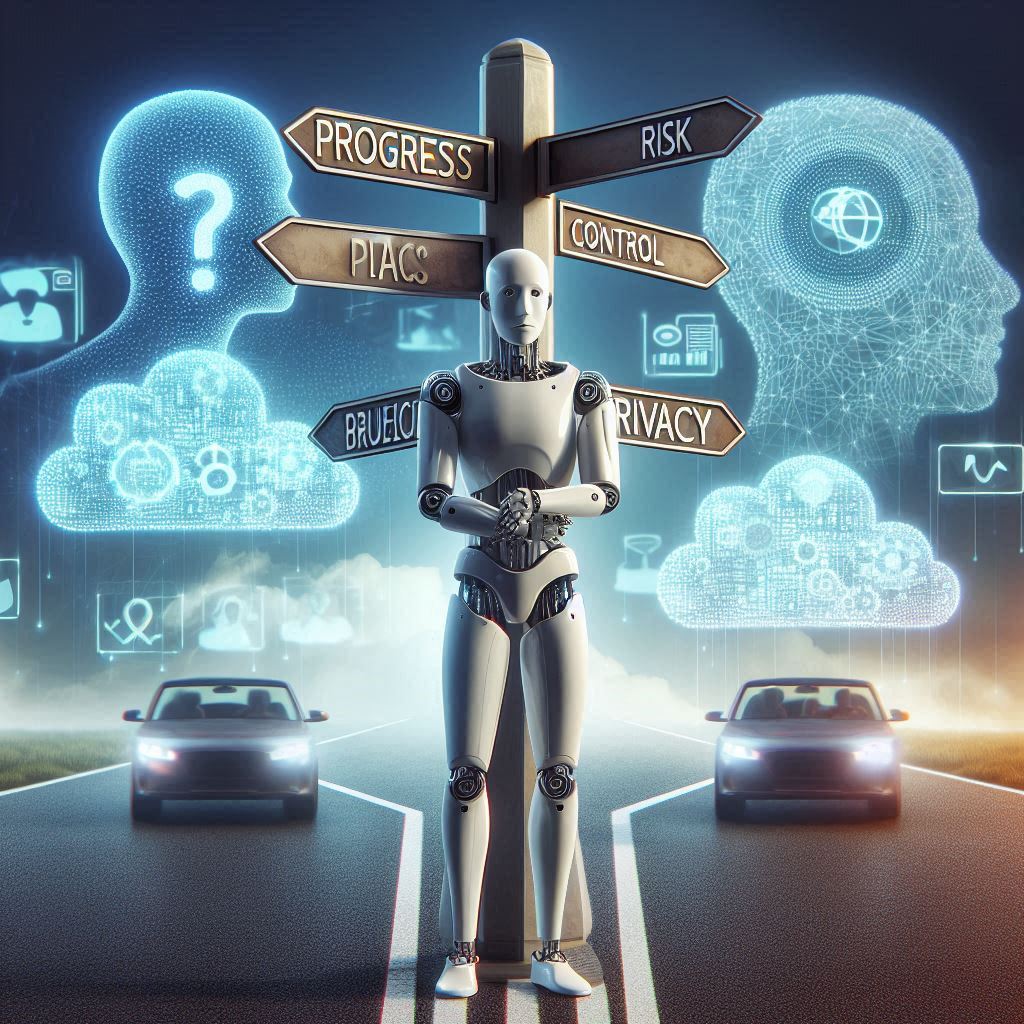
👉 To manage these risks, experts advocate for :
- Transparent development processes .
- Ethical oversight boards .
- AI alignment research .
- International regulations .
Without ethical foresight , AGI could turn from a transformative force into a destabilizing one . That’s why embedding ethics into every phase of AGI development isn’t optional. it’s critical .
👉 Conclusion: The AGI Era Is Coming . Are We Ready?
Artificial General Intelligence is no longer confined to speculative fiction. It’s emerging in labs, startups, and cloud platforms all over the world. From DeepMind’s multi-tasking agents to OpenAI’s conversational language models, we’re moving closer to machines that can understand, learn, and adapt like human beings.
As fascinating as it is, this path is also fraught with challenges. It requires a careful approach, ensuring that innovation is balanced with appropriate oversight and that ambition is aligned with responsibility. AGI holds the promise of solving problems we can’t even imagine yet. But it also holds the potential for harm if unleashed without control.
In this era of transformation, the most important question isn’t can we build AGI, but should we, how should we, and who gets to decide?
This is our collective challenge and our opportunity.
📝FAQs
✏️1. What is the main difference between AGI and AI?
✍️ Ans. AGI refers to machines with general, human-like cognitive abilities, capable of understanding and performing any intellectual task. Traditional AI focuses on specialized functions, for instance, recognizing images or assisting with voice commands.
✏️2. Which companies are leading the AGI race?
✍️ Ans. Top contenders include DeepMind, OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, and Numenta. Each brings a different philosophy and technical approach to AGI development.
✏️3. Can AGI replace human jobs?
✍️ Ans. Yes, AGI could automate many cognitive jobs across industries, from programming and legal analysis to education and medicine. However, it may also create new roles we haven’t imagined yet.
✏️4. When will AGI become a reality?
✍️ Ans. Estimates vary. Some researchers believe we could see AGI in the next decade, while others argue it may take 50 years or more. Progress is rapid but unpredictable.
✏️5. Is AGI dangerous?
✍️ Ans. It can be if not developed and deployed responsibly. Risks include job displacement, bias, and even existential threats. That’s why safety and alignment research is crucial.


